 Home
Home
 Back
Back
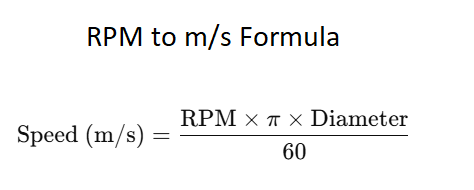
RPM (Revolutions Per Minute) and m/s (meters per second) are two units used to describe the rotational or linear speed of an object. There is a relationship between them, but the specific conversion depends on factors such as the radius of rotation and the presence of a gear ratio. Below is a detailed explanation of the relationship between RPM and m/s.
RPM stands for Revolutions Per Minute, representing the number of rotations per minute. It is an important metric for describing the performance of rotating machinery, such as motors, fans, and wheels.
m/s stands for meters per second, representing the distance an object travels per second. In circular motion, linear speed refers to the instantaneous speed of a point moving along the circumference.
The relationship between RPM and m/s can be expressed using the following formula:
Linear Speed (m/s) = π × Rotation Radius (m) × RPM / 30
Or simplified as:
1 RPM = 2πR / 60 (m/s), where R is the rotation radius in meters.
This formula shows that the linear speed of an object is proportional to its rotation radius and RPM. The larger the rotation radius or the higher the RPM, the faster the linear speed.
In practical applications, rotating devices such as motors may be equipped with gear reducers to alter the output shaft's speed and torque. If a gear ratio is present, the RPM must be adjusted accordingly. For example, if a motor has a gear ratio of 1:19, the actual RPM output to the wheel will be 1/19 of the motor's RPM.
Assume a motor speed of 400 RPM, a wheel diameter of 185 mm (radius of 92.5 mm or 0.0925 m), and a gear ratio of 1:19. The wheel's speed can be calculated as:
Wheel Speed = 400 × (2π × 0.0925 / 2) / 19 / 60 ≈ 0.204 m/s