 Home
Home
 Back
Back
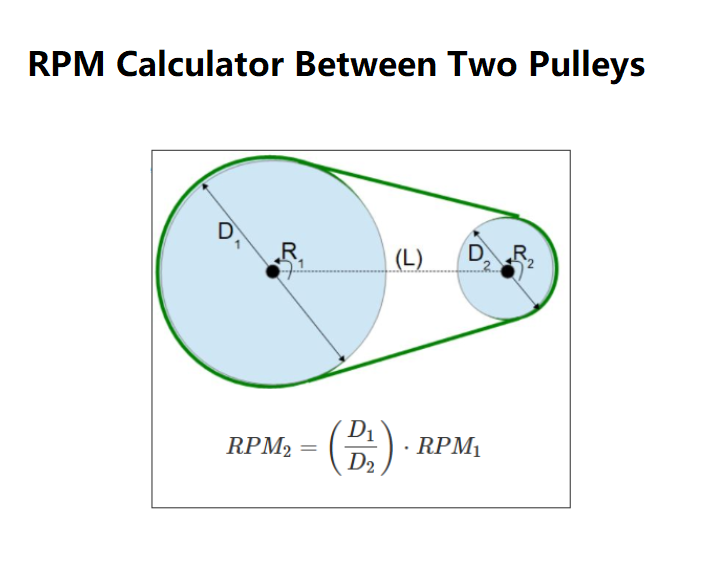
The RPM (Revolutions Per Minute) relationship between two pulleys can be calculated based on their diameters and rotation rates. The formula is as follows:
\( RPM_2 = RPM_1 \cdot \frac{D_1}{D_2} \)
- \( D_1 \): Diameter of the first pulley (in meters).
- \( RPM_1 \): Rotation rate of the first pulley (in revolutions per minute).
- \( D_2 \): Diameter of the second pulley (in meters).
- \( RPM_2 \): Rotation rate of the second pulley (to be calculated).
If the diameter of the first pulley (\( D_1 \)) is 0.5 m, the RPM of the first pulley (\( RPM_1 \)) is 120 RPM, and the diameter of the second pulley (\( D_2 \)) is 1.0 m, the RPM of the second pulley would be:
\( RPM_2 = 120 \cdot \frac{0.5}{1.0} = 60 \, \text{RPM} \)
This calculator helps determine the RPM of a second pulley based on the diameters and rotation rates of both pulleys, useful in mechanical and engineering applications.
Yes, the calculator supports various units for rotation rate, including RPM, radians/second, degrees/second, and more. All inputs are converted to RPM for accurate calculations.
The calculator accepts diameter inputs in meters, centimeters, inches, feet, and yards, and automatically converts them to meters for the calculation, with results provided in multiple units.
Entering zero for any RPM value will result in no calculation, as division by zero is undefined. Please ensure all RPM values are greater than zero.
The results are displayed in multiple units (meters, centimeters, millimeters, feet, inches, yards) for convenience, allowing you to use the value in your preferred unit.